World Immunization Day, observed annually on November 10, aims to raise awareness about the vital role vaccines play in preventing infectious diseases and protecting public health. Immunization is one of the most effective and cost-efficient intervention for controlling and eradicating diseases, saving millions of lives globally each year. Vaccines help protect individuals from diseases like measles, polio, tuberculosis, and COVID-19. By reducing the incidence of infectious diseases, immunization not only safeguards individuals but also strengthens community health by building herd immunity. This day encourages governments, healthcare providers, and communities worldwide to emphasize the importance of vaccines and extend immunization coverage, especially to underserved populations.
In India, World Immunization Day is particularly significant due to the unique challenges the country faces in reaching remote areas. Further, children, in particular, remain at significant risk because they are either unimmunized or partially immunized against vaccine-preventable diseases. Partially immunized and unimmunized children are most susceptible to childhood diseases and are at a much higher risk of dying as compared to fully immunized children.
Immunization has been a central focus in India’s public health strategy for decades, leading to remarkable progress in reducing disease prevalence and child mortality rates. World Immunization Day thus serves as an opportunity to reaffirm India’s commitment to achieving universal immunization and to reflect on the progress made through landmark initiatives, including the Universal Immunization Programme and Mission Indradhanush. This day also highlights the need for continued efforts to ensure every individual has access to life-saving vaccines.
Universal Immunization Programme (UIP)
The Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) is one of India’s most comprehensive public health initiatives, aiming to provide life-saving vaccines to millions of newborns and pregnant women each year. Initially launched in 1978 as the Expanded Programme on Immunization, it was rebranded as the UIP in 1985 when its coverage was extended beyond urban centres to rural areas, addressing disparities in healthcare access. In 1992, the UIP was incorporated into the Child Survival and Safe Motherhood Programme and later, in 1997, into the National Reproductive and Child Health Programme. Since 2005, under the National Rural Health Mission, the UIP has become a central component of India’s public health efforts, focusing on ensuring that vaccines reach every child, even in the most remote parts of the country.
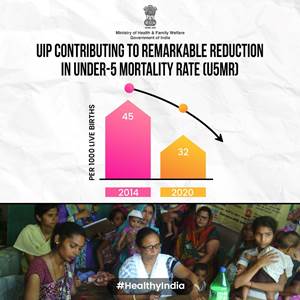
With a targeted annual reach of around 2.67 crore newborns and 2.9 crore pregnant women, the UIP has become one of the most cost-effective health interventions in the country, significantly reducing the under-5 mortality rate from 45 per 1000 live births in 2014 to 32 per 1000 live births (SRS 2020). With consistent efforts to reach and vaccinate all eligible children against vaccine-preventable diseases, the country’s Full Immunization Coverage for FY 2023-24 stands at 93.23% nationally. (state-wise Full Immunization Coverage for FY 2023-24)

Currently, the program provides free immunization against 12 diseases, including nine nationwide, such as Diphtheria, Tetanus, Polio, Measles, and Hepatitis B. Additionally, it offers vaccines against Rotavirus diarrhoea, Pneumococcal Pneumonia, and Japanese Encephalitis in specific regions. Under this initiative, a child is considered fully immunized after receiving all vaccinations as per the national schedule within the first year of life. Notable milestones include India’s elimination of polio in 2014 and maternal and neonatal tetanus in 2015, achievements that underscore the impact of the UIP in protecting public health.
Mission Indradhanush Mission Indradhanush (MI), launched in December 2014, is a strategic initiative by the Indian government aimed at increasing the full immunization coverage for children across the country, with a goal to reach 90% coverage. Mission Indradhanush specifically focuses on areas with low immunization rates, including hard-to-reach regions and communities where children are either unvaccinated or partially vaccinated. This mission adopts a targeted approach, prioritizing districts and pockets where immunization levels remain low, thereby striving to bridge critical gaps in vaccine coverage and ensuring that no child is left unprotected. Since its inception, twelve phases of Mission Indradhanush have been completed, covering 554 districts nationwide.

Mission Indradhanush has been integrated into other significant national programs, such as the Gram Swaraj Abhiyan and the Extended Gram Swaraj Abhiyan, further enhancing its outreach. Under these programs, immunization efforts extended to 16,850 villages across 541 districts and 48,929 villages across 117 aspirational districts, respectively. The first two phases of Mission Indradhanush alone led to a 6.7% increase in full immunization coverage in just one year, reflecting its early success.
The U-WIN Portal represents a major leap forward in India’s immunization efforts, providing a fully digitized record of vaccination for pregnant women and children from birth to 17 years under the Universal Immunization Programme. This digital platform aims to streamline vaccine delivery and record-keeping, ensuring that every individual can easily access and manage their immunization records. Designed with user-friendly, citizen-centric services, U-WIN allows for ‘Anytime Access’ and ‘Anywhere’ vaccination, offering flexible scheduling options for recipients. Citizens can self-register through the U-WIN web portal or the mobile app, which makes it easier for families to keep track of vaccination schedules and receive automated SMS alerts for upcoming doses. The platform also generates a universal QR-based eVaccination Certificate and provides the option to create an Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) ID for themselves and a Child ABHA ID for their children, enabling comprehensive digital health management.
With accessibility in mind, the U-WIN portal is available in 11 regional languages, including Hindi, to ensure widespread usability across diverse linguistic communities. As of September 16, 2024, the platform has registered 6.46 crore beneficiaries, conducted over 1.04 crore vaccination sessions, and recorded 23.06 crore administered vaccine doses. This scale of registration and record-keeping highlights U-WIN’s impact in making immunization data readily accessible and securely stored for millions of families across the country. The platform’s broad capabilities demonstrate India’s commitment to leveraging technology to enhance healthcare accessibility, streamline immunization tracking, and further strengthen public health infrastructure at the grassroots level.
India’s journey in public health showcases remarkable achievements in the elimination of several deadly diseases. From being officially certified polio-free to eradicating maternal and neonatal tetanus, the country has made significant strides in improving the health and well-being of its citizens. The country’s proactive efforts in disease control and vaccination, backed by strong infrastructure and international collaboration, have set global benchmarks. India’s successes in immunization programs highlight its growing capacity to tackle vaccine-preventable diseases and contribute to global health security.

India’s Public Health Milestones
India’s public health journey is marked by significant achievements, including the world’s largest COVID-19 vaccination drive. From becoming polio-free to eradicating maternal and neonatal tetanus, the country has made great strides in improving health outcomes. Strong infrastructure, proactive disease control efforts, and international collaboration have helped India set global benchmarks in tackling vaccine-preventable diseases.
- India’s Covid Vaccination Drive
India’s COVID-19 Vaccination Programme, launched on January 16, 2021, stands as a global success story in public health. By January 6, 2023, the program had administered over 220 crore doses, covering 97% of eligible citizens with at least one dose and 90% with both doses. Initially focused on the adult population, the program expanded to include younger age groups, with vaccinations for those aged 12-14 beginning on March 16, 2022, and precautionary doses for individuals aged 18-59 starting on April 10, 2022.
Overcoming significant challenges, the program required rapid vaccine research, the training of 2.6 lakh vaccinators and 4.8 lakh support members, and the establishment of an IT platform for tracking and delivery. This proactive approach enabled India to not only meet domestic needs but also support global vaccination efforts through initiatives like Vaccine Maitri, which supplied vaccines to other nations.
On March 27, 2014, India, along with ten other countries in the WHO South-East Asia Region, was officially certified as polio-free—a significant public health achievement. India’s last reported case of polio was on January 13, 2011, in Howrah, West Bengal. However, despite this certification, the country remains vigilant due to the persistent risk of poliovirus importation from the two countries where polio remains endemic: Afghanistan and Pakistan.
India’s successful fight against polio has strengthened its broader immunization infrastructure, which is now being leveraged to protect against a range of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (VPDs). Under the Universal Immunization Programme (UIP), the country continues to introduce additional vaccines, aiming to ensure that no child is left unprotected.
The systems developed during the National Polio Program have greatly enhanced routine immunization efforts, setting a goal of over 90% full immunization coverage. This progress is a collaborative effort supported by state governments, WHO, UNICEF, Rotary International, and other partners, who have been instrumental in not only eradicating polio but also in advancing India’s immunization initiatives for broader public health security.
- Elimination of Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus (MNTE)
India’s success in eliminating maternal and neonatal tetanus (MNTE) stands as a major public health accomplishment. Achieved in April 2015, well ahead of the global target of December 2015, MNTE validation was completed across all of India’s 36 states and union territories. This milestone signifies that the incidence of maternal and neonatal tetanus has fallen to less than 1 case per 1,000 live births, effectively eliminating it as a public health problem. This achievement reflects India’s commitment to safe maternal and newborn health practices through health system strengthening, high routine immunization coverage, clean delivery protocols, and strong surveillance. It is a testament to the dedication of health workers, policymakers, and all stakeholders involved.
In another historic milestone, India became the first country to be officially recognized as yaws-free by the World Health Organization (WHO), achieving this well before the global target year of 2020. This recognition highlights India’s proactive and sustained efforts to eradicate the disease, which primarily affects rural and marginalized communities. The elimination of yaws reflects comprehensive public health efforts focused on early treatment, health education, and targeted interventions for vulnerable populations. WHO and UNICEF lauded India’s achievements, noting the wider impact on community health, socio-economic improvement, and India’s continued leadership in global public health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, India’s commitment to immunization reflects a holistic approach to safeguarding public health, with a focus on reaching every individual, especially those in underserved and remote areas. Through initiatives like the Universal Immunization Programme, Mission Indradhanush, and the U-WIN portal, the country has made remarkable strides in increasing immunization coverage, combating vaccine-preventable diseases, and reducing child mortality. India’s successful elimination of polio, its resilient response to the COVID-19 pandemic, and its dedication to leveraging technology for healthcare access underscore the nation’s capacity to meet complex health challenges. As World Immunization Day reminds us of the vital role vaccines play in public health, India stands as an example of what can be achieved with comprehensive planning, community engagement, and a commitment to universal access. Continued efforts will be essential to maintaining and expanding these achievements, ensuring that no child is left unprotected and every individual has access to life-saving vaccines for a healthier future.
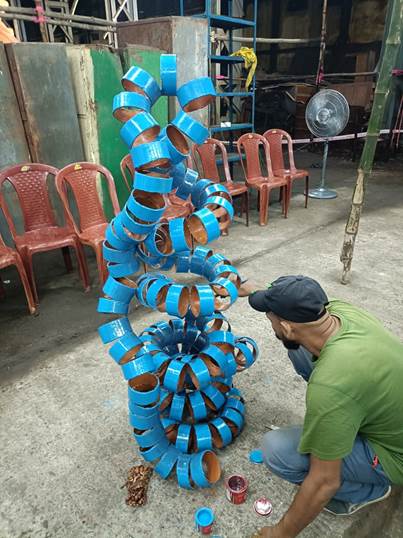





















 FSD Mon employees meticulously cleaned areas overgrown with grass, bushes and bamboo at FSD Mon, transforming the space into a spotless environment. In a remarkable display of creativity and sustainability, depot staff repurposed the bamboo to craft a functional dustbin, exemplifying the ‘Waste to Wonder’ art.
FSD Mon employees meticulously cleaned areas overgrown with grass, bushes and bamboo at FSD Mon, transforming the space into a spotless environment. In a remarkable display of creativity and sustainability, depot staff repurposed the bamboo to craft a functional dustbin, exemplifying the ‘Waste to Wonder’ art.
