Summary:The flow of genes between Bengal tigers in two reserves of the Terai Arc Landscape in western Himalayan foothills is too low, according to a study.
The flow of genes between Bengal tigers in two reserves of the Terai Arc Landscape in western Himalayan foothills is too low, according to a study published April 26, 2017 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Surendra Prakash Goyal from Wildlife Institute of India, India, and colleagues.
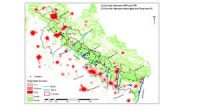
Tigers are endangered partly due to habitat loss, which can fragment populations and reduce gene flow among them. Gene flow between populations can maintain genetic variation and spread beneficial gene alleles, so understanding the gene flow of isolated tiger populations i.e. in western Himalayan foothills is crucial in developing management strategies for conserving these big cats. Goyal and colleagues analyzed DNA from 71 samples of tissue, blood or scat from Bengal tigers to assess their gene flow in an 1,800-square-kilometer region of the western Himalayan foothills. The region has two main subpopulations of tigers, one in the Rajaji Tiger Reserve and the other in the Corbett Tiger Reserve.
The researchers found that tiger gene flow between two reserves was asymmetrical and was lower than in previous reports in other tiger populations. Functionality of the corridor (C1 and C2 map) could remain viable if habitat quality does not deteriorate any more. However, given changing land use in the connecting corridor, the gene flow was inadequate. The authors suggest that measures to maintain connectivity between the tiger reserves could include relocating villages and industries, reducing human dependency, banning sand and boulder mining in the corridors.
More: Science







Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.